Treatments
The purpose of an operation on the pancreas is to remove the affected part of the pancreas that contains, for example, a tumor.
The most common pancreatic surgeries are:
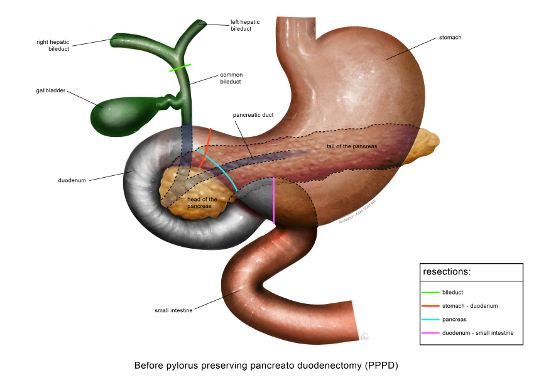
- a pancreatic head removal (pancreato-duodenectomy, or Whipple surgery)
- a pancreatic tail removal (with or without removal of the spleen)
Because the pancreas is very closely intertwined with surrounding tissues and organs, pancreatic surgery for a malignant tumor is often an extensive procedure.
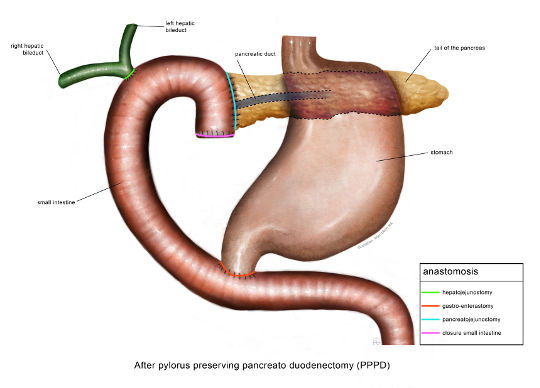
In a Whipple operation, in addition to the pancreatic head, the last part of the stomach, the duodenum, the gallbladder and a large part of the bile duct are also removed. After this, diversions are made from the small intestine to the duct of the pancreas, to the bile duct and to the stomach, to restore digestion. A new technique is to perform the Whipple operation via keyhole surgery and with the help of a surgical robot.
With pancreatic tail surgery it is sometimes unavoidable to have to remove the spleen. Pancreatic tail surgery can often be performed with keyhole surgery (laparoscopic pancreatic tail resection). We also sometimes use the operating robot.
In benign conditions, such as chronic pancreatitis, or in less rapidly or extensively growing tumors such as an insulinoma, sparing pancreatic surgery can be considered.
Examples of this are:
- an enucleation (only the tumor itself is removed, e.g. in an insulinoma), or;
- a sparing pancreatic head resection, without removal of the duodenum (also called Frey or Beger surgery, just for pancreatitis);
- the creation of a diversion from e.g. small intestine to the pancreas.
The medical specialist will discuss with you at the outpatient clinic which operation will need to be performed on you. The doctor will also discuss with you whether it is possible or desirable to perform this operation by means of keyhole surgery or with a robot operation. The medical specialist you speak to at the outpatient clinic is not always the one who will operate on you. The team discusses the details of each patient. Your surgeon will introduce himself to you before the operation.
The surgeons of the Erasmus MC pancreatic center perform more than 100 pancreatic operations every year, which means they have a lot of experience.
We try to keep the waiting time until the operation as short as possible, but sometimes there may be a few weeks waiting time due to several patients who need to be treated. We understand your wish to be helped as soon as possible and we do our utmost to schedule your surgery as soon as possible. Although it may feel that way, a few weeks earlier or later will not affect the outcome of your treatment. For benign conditions, the waiting time can sometimes be longer than average, because priority must be given to patients who are being treated for a malignant tumor.
The duration of the operation depends on the extent of the procedure, but will usually be between 3 and 6 hours. If an extensive operation has been performed, you will stay overnight in a special ward after the operation to be able to monitor you as closely as possible. We call this the PACU, the Post Anesthesia Care Unit that is located in the operating theater complex.
Pancreatic surgery is major surgery. It is important that you are in good shape. Our dietician will help you to maintain your weight. Our anesthesiologist will assess your overall health in relation to the anesthesia. Our nurse specialists are your regular point of contact during the preparation of the operation and after discharge from hospital. They will meet you during a special appointment at our outpatient clinic. All your questions and details about the operation will then be discussed with you again.
There may be complications after surgery. There is a risk of infections, leakage from the new connections and bleeding.
Due to changes in the digestive system, you may experience problems with nutrition such as delayed gastric emptying or fatty diarrhea due to a deficiency of pancreatic enzymes. Diabetes can also develop. It is important that you ensure a healthy and fiber-rich diet. Your doctor will prescribe medication for fat digestion enzymes and, if necessary, medication for diabetes.
These problems may lessen or disappear over time with the body's adjustment but usually changes to diet or medication will remain necessary over the longer term.
Sometimes pancreatic surgery is not possible, not necessary, or not enough. Complementary or alternative treatments are aimed at inhibiting the disease, reducing the chance of a tumor recurrence or metastasis, and reducing symptoms.